Event driven architecture is a design pattern built around the production, detection and reaction to events that take place in time.
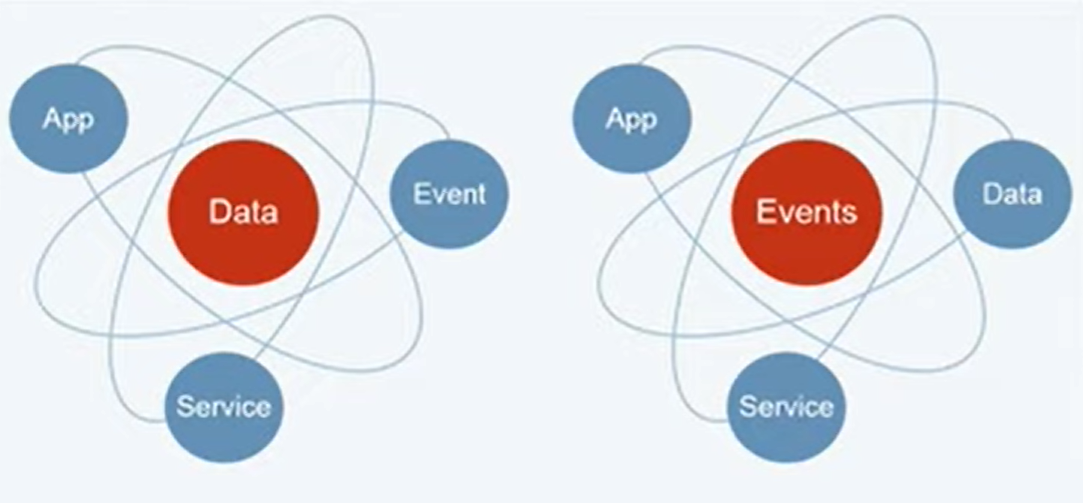
Historically business applications tend to be data centric where everything is in databases, The priority was you always had a valid copy of your data, your business was essentially in your database. But that doesn’t always lend itself to responsive applications that needs to give you information kind of in the moment.
So another way of designing business applications is event-driven. Essentially where the data is all in flight. So it’s all flying around between each of the pieces of software and the first priority is that the system remains responsive
Imagine a application where you need to make a payment and you call an API saying “submit this payment”, you receive a success response but it takes some time to actually complete the payment in the background. So it’s not a synchronous call.
However, You wouldn’t want to wait until it’s finished or to poll to constantly ask “is the payment complete”. It would be preferable to move-on and even better to receive an event notifying you when it’s done. This was example of an responsive interaction which is event driven.
Pros 👍
Loose coupling
Services do not need to be dependent on each other.
Scalability
Since the services are no longer coupled, the throughput of service 1, no longer needs to meet the throughput of service 2.
Asynchronicity
Since services are no longer dependent on a result being returned synchronously, a fire and forget model can be used, which can greatly speed up a process. Although this can have downsides.
Point in time recovery
If events are backed by a queue or maintaining some kind of history, it is possible to replay events, or even go back in time and recover state.
Cons 👎
Over-engineering of processes
Sometimes a simple call from one service to another is enough. If a process uses event driven architecture, it usually requires more infrastructure and work to support it.
Inconsistencies
Because processes now rely on eventual consistency, it is not typical to support ACID transactions, so handling of duplications, or out of sequence events can make service code more complicated, harder to test and debug all situations.
Summary 📝
This is a basic introduction of Event Driven, there are other benefits to using Event driven architecture such as a reversal of dependencies and high responsiveness.
Furthermore there are many challenges to consider when consuming Event Driven systems as well which I may write another post on.
